Arduino Hardware Notes
Power Supply parts
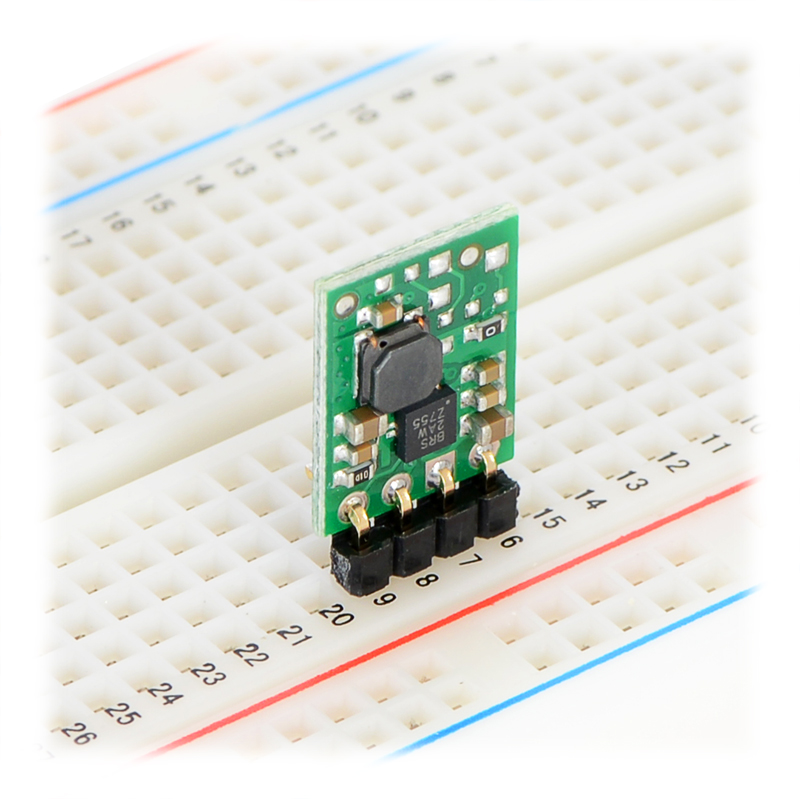
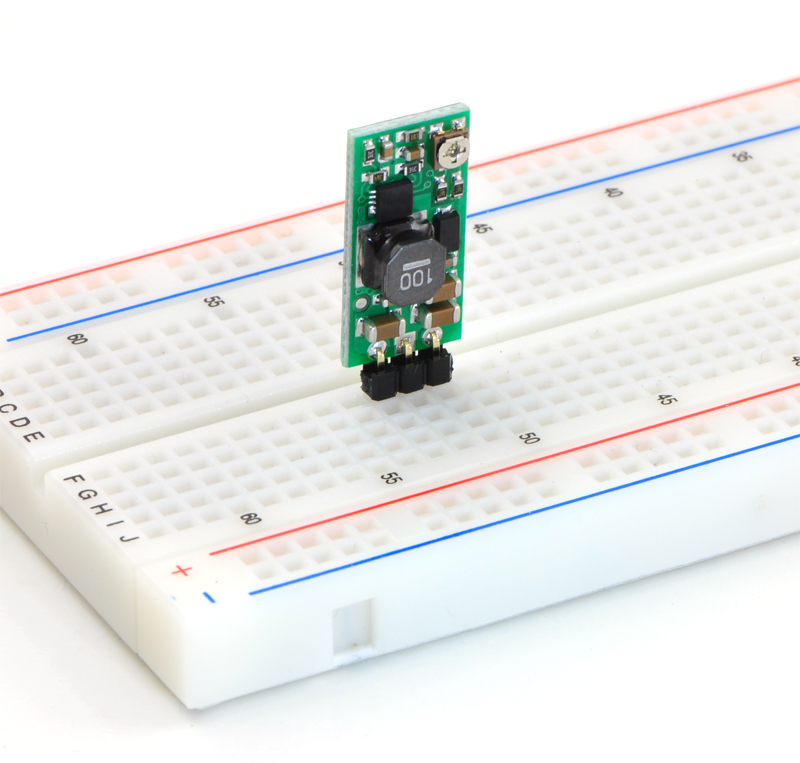
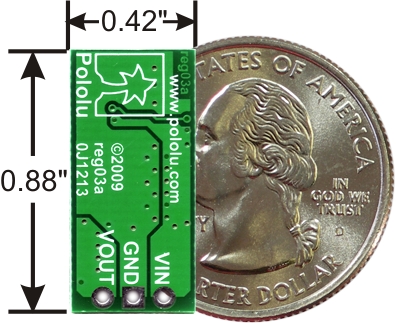
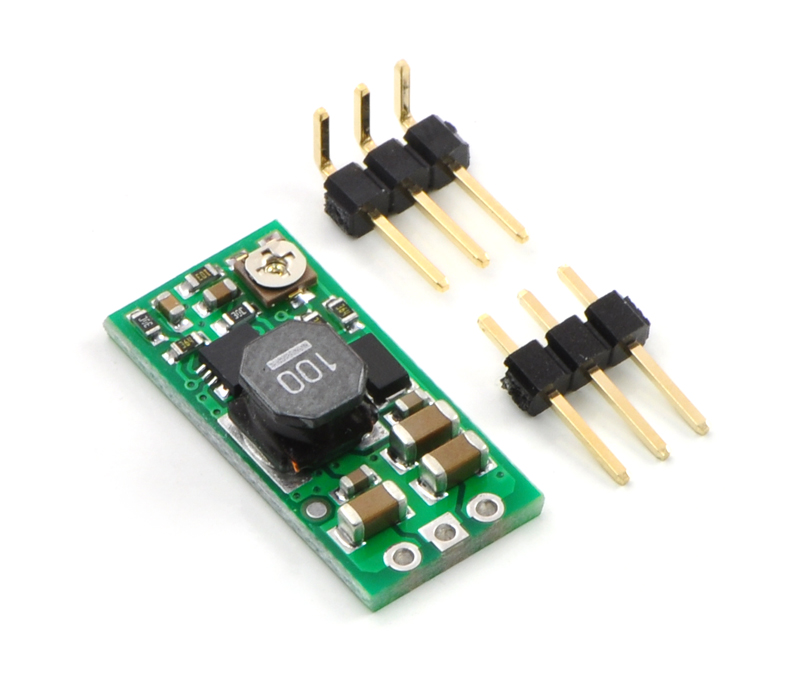
Pololu Adjustable Boost Regulator 2.5-9.5V
$11.95
Overview
The Pololu adjustable boost regulator is a very flexible switching regulator (also called a switched-mode power supply, SMPS, or DC-to-DC converter) that can generate voltages higher than its input voltage. We offer two adjustable ranges: approximately 2.5 V to 9.5 V and 4 V to 25 V. The output voltage can be set using the trimmer potentiometer in the upper-right corner of the board. The input voltage range is 1.5 V to 16 V (the input voltage should be kept below the output voltage). The integrated 2 A switch allows for output currents high enough to drive small motors, as in our 3pi robot, and allows large voltage gains, such as obtaining 24 V from two NiMH or NiCd cells.
Some example applications include:
- Powering 5 V or 3.3 V systems from lower-voltage batteries
- Powering 5 V subsystems (e.g. sensors) in lower-voltage (e.g. 3.3 V) systems
- Achieving consistent actuator operation when powered by fluctuating batteries
- Powering high-brightness LEDs or a large number of LEDs in series
Feature summary
- input voltage: 1.5 V to 16 V
- output adjustable from 2.5 V to 9.5 V or 4 V to 25 V
- 750 kHz switching frequency
- 2 A switch (and input) limit
- integrated over-temperature and over-current shutoff
- typical efficiency of 80-90% when doubling voltage and with 100-500 mA output
- small size: 10.7 x 22.4 x 5.8 mm (0.42″ x 0.88″ x 0.23″)
- weight without header pins: 1.6 g (0.06 oz)
Feature summary
- input voltage: 1.5 V to 16 V
- output adjustable from 2.5 V to 9.5 V or 4 V to 25 V
- 750 kHz switching frequency
- 2 A switch (and input) limit
- integrated over-temperature and over-current shutoff
- typical efficiency of 80-90% when doubling voltage and with 100-500 mA output
- small size: 10.7 x 22.4 x 5.8 mm (0.42″ x 0.88″ x 0.23″)
- weight without header pins: 1.6 g (0.06 oz)
Connections
The boost regulator has just three connections: the input voltage, ground, and the output voltage. These three connections are labeled on the back side of the PCB, and they are arranged with a 0.1″ spacing along the edge of the board for compatibility with standard solderless breadboards and perfboards and connectors that use a 0.1″ grid. You can solder wires directly to the board or solder in either the 3×1 straight male header strip or the 3×1 right-angle male header strip that is included.
Setting the output voltage
The output voltage can be adjusted using a meter and a light load (e.g. a 10 kΩ resistor). Turning the potentiometer clockwise increases the output voltage. The output voltage can be affected by a screwdriver touching the potentiometer, so the output measurement should be done with nothing touching the potentiometer.
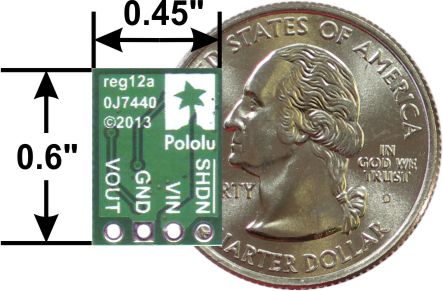
Pololu 5V Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V11F5
$4.95
This compact (0.45″×0.6″) U1V11F5 switching step-up (or boost) voltage regulator efficiently generates 5 V from input voltages as low as 0.5 V. Unlike most boost regulators, the U1V11F5 offers a true shutdown option that turns off power to the load, and it automatically switches to a linear down-regulation mode when the input voltage exceeds the output. The pins have a 0.1″ spacing, making this board compatible with standard solderless breadboards and perfboards.
Overview
This 5 V boost (step-up) voltage regulator generates higher output voltages from input voltages as low as 0.5 V, and it also automatically switches to a linear down-regulation mode when the input voltage exceeds the output. This makes it great for powering 5 V electronics projects from 1 to 3 NiMH, NiCd, or alkaline cells or from a single lithium-ion cell. Additionally, unlike most boost regulators, this unit offers a true shutdown option that turns off power to the load (with typical boost regulators, the input voltage will pass directly through to the output when they are disabled).
When boosting, this module acts as a switching regulator (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) and has a typical efficiency between 70% to 90%. The available output current is a function of the input voltage, output voltage, and efficiency (see Typical Efficiency and Output Current section below), but the input current can typically be as high as 1.2 A.
Features
- Input voltage: 0.5 V to 5.5 V
- Fixed 5 V output with 4% accuracy
- True shutdown option that turns off power to the load
- Automatic linear down-regulation when the input voltage is greater than the output voltage
- 1.2 A switch allows for input currents up to 1.2 A
- Good efficiency at light load: <1 mA typical no-load quiescent current, though it can exceed 1 mA for very low input voltages (<100 μA typical quiescent current with SHDN = LOW)
- Integrated over-temperature shutoff
- Small size: 0.45″ × 0.6″; × 0.1″ (12 × 15 × 3 mm)
Connections
The boost regulator has four connections: shutdown (SHDN), input voltage (VIN), ground (GND), and output voltage (VOUT).
The SHDN can be driven low (typically under 0.4 V) to power down the regulator and turn off power to the load (unlike most boost regulators, the input power does not pass through to the output when the board is disabled). This pin is internally pulled up to VIN through an 100 kΩ resistor, so it can be left disconnected or connected directly to VIN if you do not need to use the disable feature. The disable threshold is a function of the input voltage as follows:
- For VIN < 0.8 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.1×VIN to disable the regulator and above 0.9×VIN to enable it.
- For 0.8 V ≤ VIN ≤ 1.5 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.2×VIN to disable the regulator and above 0.8×VIN to enable it.
- For VIN > 1.5 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.4 V to disable the regulator and above 1.2 V to enable it.
- The input voltage, VIN, must be at least 0.5 V for the regulator to turn on. However, once the regulator is on, the input voltage can drop as low as 0.3 V and the 5 V output voltage will be maintained on VOUT. Unlike standard boost regulators, this regulator has an additional linear down-regulation mode that allows it to convert input voltages as high as 5.5 V down to 5 V for small to moderate sized loads (for example, in our tests, the adjustable version of this regulator was able to supply 300 mA while converting an input of 5.5 V down to 1.8 V). When the input voltage exceeds 5 V, the regulator automatically switches to this down-regulation mode. The input voltage should not exceed 5.5 V. Please be wary of destructive LC spikes that might cause the input voltage to surpass 5.5 V (see below for more information).